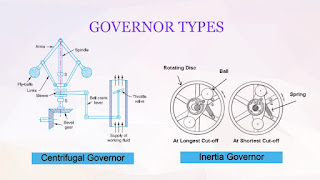
Basic principle of solar energy:
The sun gives out 3.7*10 ^20 MW of energy into
space, out of which earth intercepts one 1.7*10^11 MW. Solar radiation is
reduced in intensity in the atmosphere by clouds, dust, haze, and fog. The
energy emitted by the sun in three minutes is equivalent to the world energy
consumption during a year. Most of the energy we receive from the sun comes in
the form of light, a short-wave radiation, not all of which is visible to human
eye. When this radiation strikes a solid or liquid, it is absorbed and
transformed into heat energy.
The heat energy is collected in a fluid,
generally water. This heat energy can be used in a solar heater or drier or can
be used to run an engine. Flat plate collector or parabolic concentrated type
collector is issued to collect and concentrate the solar energy and increase
the temperature of the working fluid.
Applications
of solar energy enjoying most success today are:
• Solar engines for water pumping.
• Solar water heaters.
• Solar cookers
• Solar furnaces.
• Photo-voltaic conversion (solar cells).
• Solar power generation.
Arrangement
of solar power plant:

The Image above shows a solar power plant with a
low temperature solar engine using heated water from flat plate solar collector
and butane as the working fluid. This was developed in France for lift
irrigation.