What Is MATLAB?
MATLAB® is a high-performance
language for technical computing. It integrates computation, visualization, and
programming in an easy-to-use environment where problems and solutions are
expressed in familiar mathematical notation.
Typical uses include
• Math and
computation
• Algorithm development
• Data acquisition
• Modelling, simulation,
and prototyping
• Data analysis, exploration, and visualization
• Scientific
and engineering graphics
• Application development, including graphical user
interface building
MATLAB is an interactive system
whose basic data element is an array that does not require dimensioning. This
allows you to solve many technical computing problems, especially those with
matrix and vector formulations, in a fraction of the time it would take to
write a program in a scalar noninteractive language such as C or Fortran.
The name MATLAB stands for matrix
laboratory. MATLAB was originally written to provide easy access to matrix
software developed by the LINPACK and EISPACK projects. Today, MATLAB engines
incorporate the LAPACK and BLAS libraries, embedding the state of the art in
software for matrix computation.
MATLAB has evolved over a period
of years with input from many users. In university environments, it is the
standard instructional tool for introductory and advanced courses in
mathematics, engineering, and science. In industry, MATLAB is the tool of
choice for high-productivity research, development, and analysis.
MATLAB features a family of
add-on application-specific solutions called toolboxes. Very important to most
users of MATLAB, toolboxes allow you to learn and apply specialized technology.
Toolboxes are comprehensive collections of MATLAB functions (M-files) that
extend the MATLAB environment to solve particular classes of problems. Areas in
which toolboxes are available include signal processing, control systems,
neural networks, fuzzy logic, wavelets, simulation, and many others.
The MATLAB System:
The MATLAB system consists of five main parts:
Development Environment. This is
the set of tools and facilities that help you use MATLAB functions and files.
Many of these tools are graphical user interfaces. It includes the MATLAB
desktop and Command Window, a command history, an editor and debugger, and
browsers for viewing help, the workspace, files, and the search path.
The MATLAB Mathematical Function
Library. This is a vast collection of computational
algorithms ranging from elementary functions, like sum, sine, cosine, and
complex arithmetic, to more sophisticated functions like matrix inverse, matrix
eigenvalues, Bessel functions, and fast Fourier transforms.
The MATLAB Language. This is a
high-level matrix/array language with control flow statements, functions, data
structures, input/output, and object-oriented programming features. It allows
both “programming in the small” to rapidly create quick and dirty throw-away
programs, and “programming in the large” to create large and complex
application programs.
Graphics. MATLAB
has extensive facilities for displaying vectors and matrices as graphs, as well
as annotating and printing these graphs. It includes high-level functions for
two-dimensional and three-dimensional data visualization, image processing,
animation, and presentation graphics. It also includes low-level functions that
allow you to fully customize the appearance of graphics as well as to build
complete graphical user interfaces on your MATLAB applications.
The MATLAB External
Interfaces/API. This is a library that allows you to write C and
Fortran programs that interact with MATLAB. It includes facilities for calling
routines from MATLAB (dynamic linking), calling MATLAB as a computational
engine, and for reading and writing MAT-files.


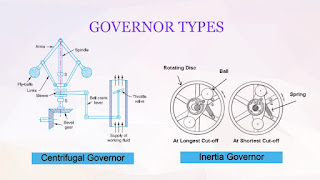






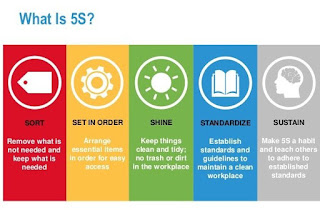





Comments
Post a Comment