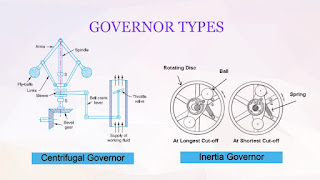
A processor, or "microprocessor," is a small chip that resides in computers and other electronic devices. Its basic job is to receive input and provide the appropriate output.The central processor of a computer is also known as the CPU, or "central processing unit." This processor handles all the basic system instructions, such as processing mouse and keyboard input and running applications. Modern CPUs often include multiple processing cores, which work together to process instructions. While these "cores" are contained in one physical unit, they are actually individual processors.
Processor speed :
A Processor provides the instruction that multiple application processes need to perform their jobs.The faster it does that, the faster a computer operates.
Clock Speed :
It may be tempting to buy a processor because it advertises a fast clock speed. However, clock speed, as Computer Shopper notes, “is only marginally useful in gauging how ‘fast’ a CPU really is.” That’s because a chip’s architecture, cache and other factors also influence your computing speed. Clock speed refers to the number of cycles that a processor executes per second. A cycle is a unit of measurement during which a processor executes instructions. If you see a processor that has a rating of 3.1 GHz, it operates at 3.1 billion cycles per second.
Cores vs. Speed
A processor’s core count can be more important than its speed. A dual-core chip consists of two processors while a quad-core chip contains four. You’ll find a quad-core chip useful if you like to run multiple applications at once or run programs designed to take advantage of four cores. Like their single-core counterparts, multi-core processors also perform faster when they have higher clock speeds.

















Comments
Post a Comment