What is Carburizing?
Carburizing is one of the most widely used methods, of case hardening. The purpose of case hardening is to increase the surface hardness of steel. In this process, the steel is introduced to a carbon-rich environment and elevated to a temperature range of 850 to 950oC for a certain amount of time. Due to this Carbon starts diffused into the surface layer of the material. The rate of diffusion depends upon the time and temperature zone at which the material is maintained.
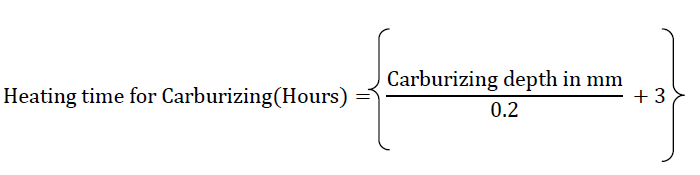
After carburizing material is quenched so that the carbon is locked in the structure. The hardness is moderately increased, but it can be hardened again through flame or induction hardening. It’s possible to carburize only a particular portion of the component(i.e.., gear tooth). The hardness achieved by Carburizing is 55 to 68 HRC and the carbon content in the surface layer is increased to 0.75 to 1.2%
The surface not to be carburized should be copper plated or covered with asbestos power mixed in fireclay cement.
Carburizing Methods
They are four basics methods of Carburizing are widely used for case hardness. They are
· Pack or Solid Carburizing
· Gas Carburizing
· Liquid Carburizing
· Vacuum Carburizing
Pack or solid Carburizing
In this process, components to be case harden is packed in an environment with high carbon content such as bone char, charcoal or barium carbonate. The components are heated to a temperature range of 850 to 950oC so that the carbon is diffused into the outer surface of the material. The diffusion rate of carbon is depending upon the composition of the part, temperature and time. The outer surface of the material is hardened whereas the core of the material remains ductile. The case hardens depth is approximately 0.1 to 2 mm.
Normally this method is used for soft steels with a carbon content of 0.2% or less which cannot be hardened by simple heating and quenching.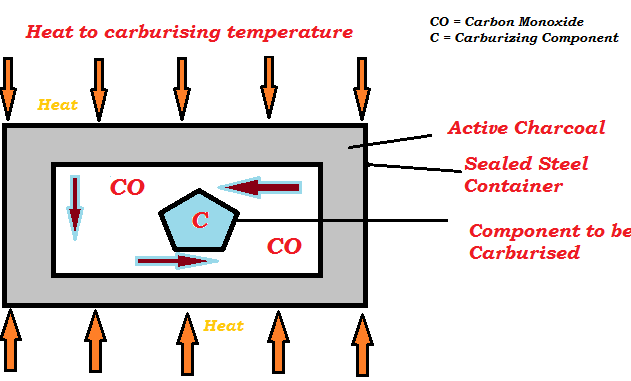

Advantages of Pack Carburizing
· It is the simplest method of Carburizing
· Less Capital cost
Gas Carburizing
This process contains gases capable of forming atomic carbon at high temperature over parts made of mild steel. The gases wildly used for this process are carbon monoxide, natural gas, a mixture of methane, ethane and propane. The components to be Carburizing is placed in a furnace and heated to a temperature range of 900 to 950oC. Then the Carburizing gas is passed through the chamber for a period of 5 to 10hours. Due to this high temperature, the carbon in the gas is diffused into the surface of the component and it is case hardened.
When compare with pack Carburizing, this method is more easy for Carburizing the components. This method can be used in mass production.
Advantages of Gas Carburizing
· It takes less time when compared with pack Carburizing method
· Control is more accurate to achieve surface carbon content and case hardness
· When compare with pack Carburizing, complicated shape components are carburised by this method.
Liquid Carburizing
In this process, the steel components are immersed in a liquefied carbon-rich bath of molten salts. The molten salt contains a mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium chloride and silicon carbide. The reaction in the bath is
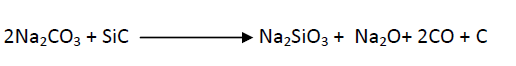
This saturates the metal with carbon. The bath is replenished from time to time. The components are immersed in the bath at a temperature of around 870 to 900oC. So that the carbon is diffused into the surface of the steel. In this method the time required for carburising the metal surface of 0.2 to 0.3mm in 35 to 55min.
Then the metal is then undergone rapid quenching to lock the carbon inside the structure. By this method uniform case hardening is obtained when compared with other methods.
Advantages of Liquid Carburizing
· Uniform case hardening depth is obtained
· Components are free from oxidation
· Soot is not formed on the surface of the component
Vacuum Carburizing
In vacuum Carburizing method, the component is placed in a very low-pressure vessel. The pressure in the vessel is maintained around 0.5 to 10 bar. The gases used in this method are acetylene, ethylene and propane. The component is heated to a temperature range of 900 to 1000oC and then the gas is passed through the vacuum chamber. The gas decomposed and the free carbon diffused into the component surface. Uniform Carburizing is obtained by this method.
The problem oxidization is reduced in vacuum Carburizing due to low oxygen present in the vacuum chamber.
Advantage of Vacuum Carburizing
· Carburizing time is very less when compared with other methods.
· Uniform Carburizing is obtained by this method.
· The oxidisation of case hardening material is reduced.













Comments
Post a Comment